In the current article, I would like to review the chain of events that occurs…
What is the meaning of mail Phishing attack in simple words? | Part 4#9
In the current article, we will continue our journey to the land of “mail threats and dangers,” and this time; our primary focus will be on one of the most dangerous and deadly types of mail attack – the Phishing mail attack!
Table of contents
- Phishing mail attack? Who, What, Where and when
- Why should I spend my time on getting to know better the character of Phishing mail attacks?
- The sophistication level of Phishing mail attack
- The basic logic of Phishing mail attack and the Phishing mail structure
- What is the “thing” that the attacker asks the victim to do?
- Plan your Phishing mail attack | step by step instructions
- The next article in the current article series
The main points that I would like to emphasize regarding Phishing mail attack are:
- The lack or the partial knowledge that we have about the characters of Phishing mail attack.
- The greater vulnerability of our mail infrastructure to Phishing mail attack.
- The greater vulnerability of our user to Phishing mail attack.
Phishing mail attack? Who, What, Where and when
Let’s start with a formal definition of Phishing mail attack as described by the Wikipedia:
Phishing is the attempt to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details (and sometimes, indirectly, money), often for malicious reasons, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication.
The word is a neologism created as a homophone of fishing due to the similarity of using a bait in an attempt to catch a victim.
Communications purporting to be from popular social websites, auction sites, banks, online payment processors or IT administrators are commonly used to lure unsuspecting victims.
Phishing emails may contain links to websites that infected with malware.
Phishing is typically carried out by email spoofing or instant messaging, and it often directs users to enter details at a fake website whose look and feel are almost identical to the legitimate one.
Phishing is an example of social engineering techniques used to deceive users and exploits the poor usability of current web security technologies.
Why should I spend my time on getting to know better the character of Phishing mail attacks?
The answer is that if we want to know of to protect our organization from Phishing mail attack, we need to know our “enemy,” the way he thinks, the way he attacks, the characters of the attack and so on.
The need to recognize the characters of Phishing mail attack is “our need,” and also “our users need.”
We need to be familiar with the characters of Phishing mail attack, so we will be able to create and configure the required defense mechanism + to be able to instruct our users.
Our users should be familiar with a Phishing mail attack so in the scenario in which the Phishing mail attack will duck our defense systems (false-negative scenario); our users, will have the knowledge that required for identifying an event of Phishing mail attack.

What is the reason for the strange term Phishing?
As a child, I loved to fish.
I have a picture in mind of an endless blue sea.
You throw the bait into the deep and blue water, and patiently wait for the “strong pull,” in which you know that the fish bit the bait.
The same concept is implemented in a Phishing attack.
The fisherman prepares the bait (the attacker creates the Phishing mail), and “throw” his bait in the big blow sea. In our scenario – the list of the destination recipients who could become his potential victims.
The fisherman (the attacker) doesn’t know if there are any fishes in the “sea” and if a particular fish decides to bite the bait.
All he can do is – waiting patiently for the “strong pull,” in which you know that the fish bit the hook.

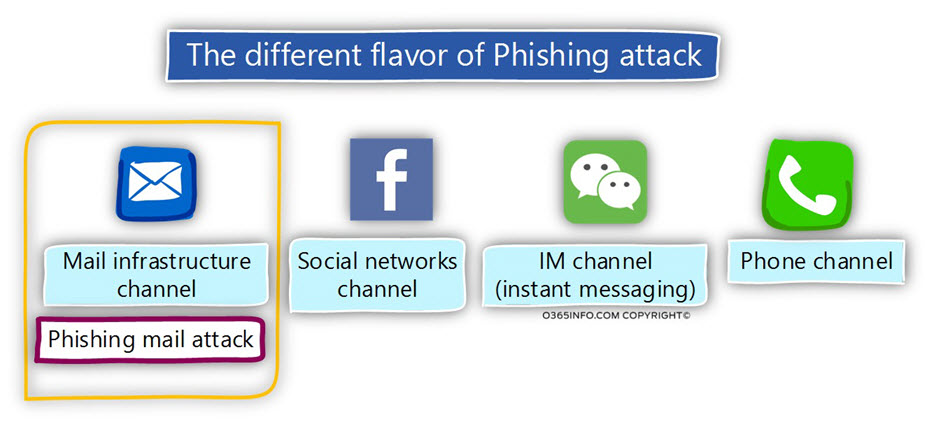
The different flavor of Phishing attack
It’s important that we will be aware of the fact that the term “Phishing attack,” is not translated automatically only to Phishing mail attack.
The opposite is true; Phishing mail attack is only a particular flavor of “Phishing attack.”
The mechanism of “Phishing attack” can be implemented via different channels such as:
- Phone channel – addressing the victim by sending him an SMS message or directly call him.
- IM (instant messaging) – addressing the victim via instant messaging applications such as Skype
- Social network channel – addressing the victim via popular social networking such as Facebook, etc.
In our specific article, we relate only to the flavor of – “Mail Phishing attack” but most of the information about the characters and the logic of “Phishing attack,” is identical to all the types of the different flavors.
The different building blocks of Phishing mail attack
Later, we will go into more specific details of the “Phishing mail attack”. For now, it’s important for me to emphasize that the term “Phishing mail attack” is translated to an “array of attack methods” that are combined and gathered into a particular channel that we describe as a Phishing mail attack.
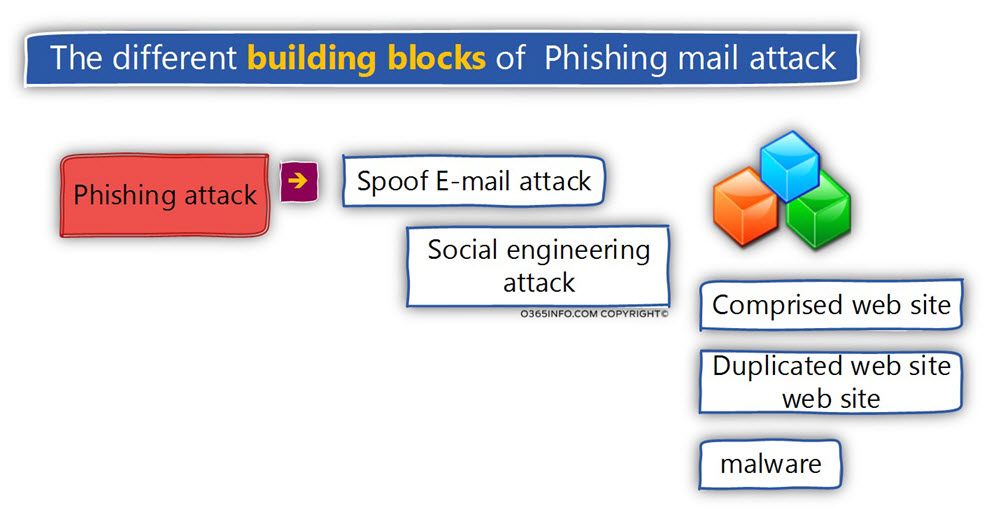
The Phishing mail attack is based on a very simple concept of – finding the weakest link in the chain and via the “weakest link” access additional territory.
For example – the Phishing mail attack was designed to use social engineering for addressing a particular human weakness. The attacker is tempting the victim “to do something” such as open a particular file.
The “specific file” is actually malware that tries to exploit an existing weakness that exists on the user desktop (now the user desktop becomes the “weakest link”).
For this reason, Phishing mail attack belongs to the notorious family of “new type of attacks” that describe as – advanced threats.

The sophistication level of Phishing mail attack
In the same way that the term “car,” can relate to many different types of “cares” begging with an old or simple car vs. a luxury car, the term “Phishing mail attack,” can relate to very simple Phishing mail attack or to a very sophisticated Phishing mail attack.
Simple Phishing mail attack
The characters of a “simple Phishing mail attack” could be translated into a simple, very easy to identify the attack because that attacker made a very little effort to execute a “professional attack.”
For example, the characters of “nonprofessional Phishing mail attack” will include the following characters.
1. Sender’s identity
The attacker will not make the required effort to use an applying identity or well-known E-mail address and instead; we use a general E-mail address from a public mail provider such a GMAIL and so on.
2. The destination recipient
The Phishing mail will be targeted to a particular recipient, or the E-mail content will not address the specific recipient by his name. Instead, the Phishing mail content will address the recipient by using a general description such as – “dear organization user”.
3. Phishing mail content
The style of the Phishing mail will be very simple and will not mimic the “look and feel” of the mail style that the “original organization” uses.
Phishing mail connects will not include a sophisticated social engineering method which should convince the victim to do something and instead, will include a very simple request such as – “please open the following file” (the malware file).
Professional Phishing mail attack
Vs. the simple Phishing mail attack, the other type of Phishing mail attack can be considered as a well-crafted, and professional Phishing mail attacks, that can easily bypass our mail security infrastructure and successfully attack our users.
For example:
1. Sender’s identity
The sender identity – the attacker can use a method in which the information about the sender looks identical (or almost identical) to the sender information that appears in a legitimate mail
The attacker can invest resources in research and find information about you and your manager and use not just a “simple identity” of the user from your organization but a very distinct identity such as your manager identity.
2. The destination recipient
The “destination victim” that the attacker tries to attack is not a random list of Potential victims, but instead, a very particular target recipient. The attacker invests the required time to learn about the company structure, the particular persons that hold a key position (CFO, CEO, etc.).
3. Phishing mail content
The attacker will invest the required resources for
- Getting a sample E-mail message from the organization which he uses his identity.
- Create an E-mail message template that looks identical to the original E-mail message style of the person which he spoofs his identity. The E-mail message style can include a specific font, the size of the font, the signature style and so on.
The level of sophistication can also be expressed in the specific social engineering method or narrative that the attacker uses as the Phishing mail content.
A Professional attacker will craft “good content” that includes a proper incentive to do the particular “thing” that’s appealing to you or relevant to you as a person.
The basic logic of Phishing mail attack and the Phishing mail structure
Regarding the subject of Phishing mail attack logic, the logic is quite simple:
The attacker tries to present an identity that can be trusted by the victim, and then, ask him to “do something” (bitten the bait) that will “activate” the attack.

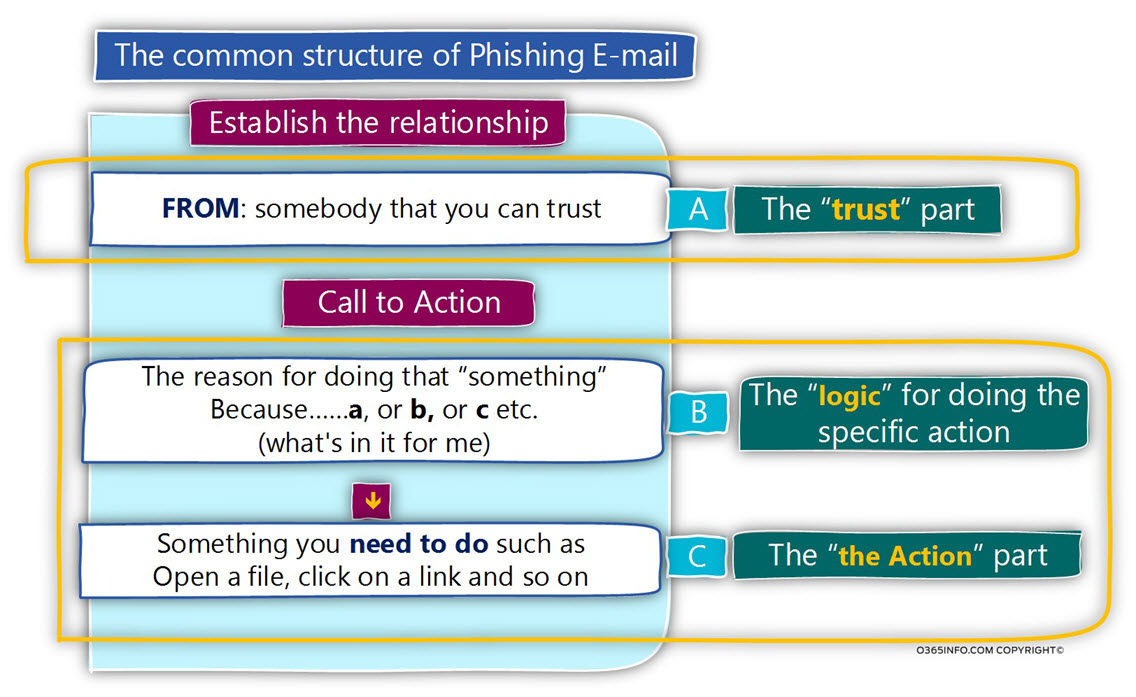
The basic structure of Phishing mail includes the flowing parts:
Part A – The “trust” part
This is the part, in which the attacker is trying to “establish a relationship” with the victim.
Very similar to the logic of a “Business Card.”
The message is – I am a reliable and trusted the person. You can trust me and trust the “thing” that I will ask you to do below.
Part B – The “Call to Action” part
This section includes two parts:
1. The “logic” for doing the concrete action
Before I ask you to do something, I want to explain and convince you to read the reason for doing the particular action.
2. The “the Action” part
This is the part, in which the attacker explicitly stated what is the “action” that he asks from the victim to do.
Most of the time, the “action” will be:
- Open a specific file (malware)
- Click on a specific link (URL) that will lead the victim to a specific Phishing website and then, “do something” when he gets to the website such as provide personal details, deposits money to a bank account, download the specific file and so on.
What is the “thing” that the attacker asks the victim to do?
Theoretically, there are endless options for the “things” that the hostile element can ask from to a victim to do. In reality, there are two major “request” that the hostile element asks most of the time:
1. Access a specific website
The Phishing mail attack includes a link (URL address) to a particular website.
The website serves as the “trap,” that the attacker had already prepared.
There could be a couple of variations to the Phishing website which the attacker is redirecting his victims too:
- A legitimate website that was compromised by the hostile element.
- A non-legitimate website that was created to mimic a legitimate website.
- A non-legitimate website which includes a forum, in which the victim fell in his details.
- A non-legitimate website which includes a malware file that the victim is asked to download and open.
- A non-legitimate website that exploits the existing vulnerability of the victim’s browser for injecting hostile code to the user desktop.
2. Click on a malware file that is attached to the Phishing mail
The other type of Phishing mail attack is straighter forward.
The attacker doesn’t convince the victim to access a particular website and then download and “activate” a specific file (malware) but instead, attached the malware directly to the E-mail message.
In case that you think – “hahaha, my mail infrastructure will block any type of executable files, and for this reason, my mail security infrastructure will prevent this scenario (a scenario in which the E-mail message includes executable file), the bad news is that in nowadays, most of the malware appear as a legitimate Innocent file such as – Microsoft Office document (Word document, Excel document and so on).

One of the most famous and deadliest Phishing mail attacks is the attack that includes the Ransomware malware that appears as a legitimate attachment.
When the victim opens the “Innocent attachment,” the malware encrypts the victim’s hard disk and asks for ransomware!

Plan your Phishing mail attack | step by step instructions
The header is a little dramatic.
Our primary purpose is not relayed to teach you how to plan and execute a successful Phishing mail attack, but instead, enable you to get into the mind of the attacker who is set in his room, and “cooking” his Phishing mail attack.
Note: In case the “title” makes you feel slightly angry because the article includes instructions that can be used by the “dark side” to become better at planning a Phishing mail attack, don’t worry.
The “bad guy” doesn’t need my help and my guidelines. They are professionals who master this field.
The life cycle of Phishing mail attack includes three major phases:
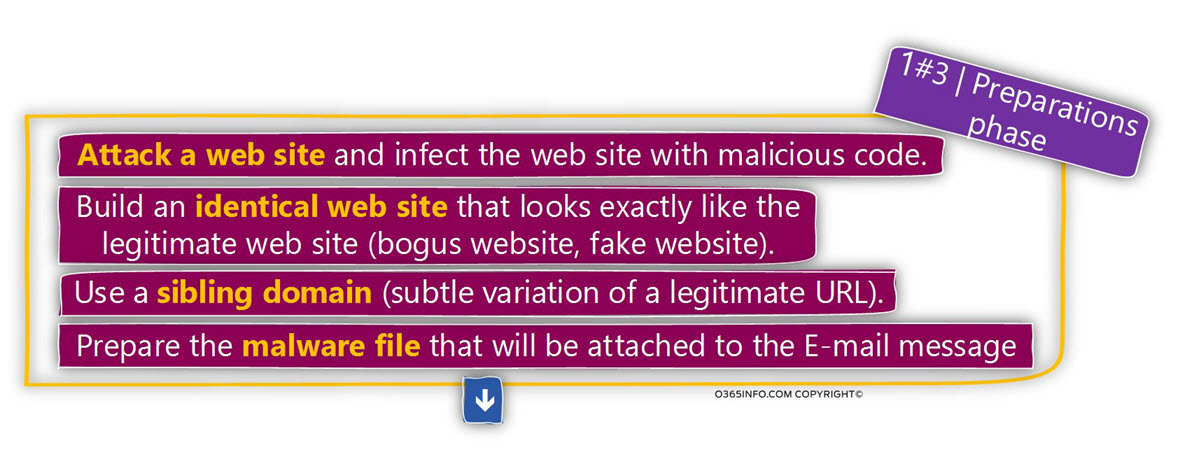
1#3 | Preparation phase
In this step, the attacker makes all the necessary preparations that will serve as the building block for the Phishing mail attacks.
Decide what are the target victims.
The attacker needs to decide who are the “destination victims.”
For example – a Phishing mail attack that will be targeting a specific organization or a particular target recipient in the organization (Spear phishing).
Another option has sent the Phishing mail attack to a harvest E-mail address list.
In a scenario of Spear phishing, the attacker will conduct research about the role of the particular recipient whom he wants to attack, his relationship with other organization users, etc.
Decide, which spoofed identity to use
The attacker can choose from a wide range of “spoofed identities” beginning with a very general sender identity, and ending with selecting a spoofed identity that uses the domain name of the target victim and even the identity of a very specific user.
For example, a Phishing mail attack in which the Phishing mail sent to the company CEO, and the spoofed identity that the attacker used is the spoofed identity of the company CFO.
Plan and design the style of the E-mail message.
In a “sophisticated” Phishing mail attack, the attacker will spend effort in crafting an E-mail message that will mimic that exact style of the “original E-mail message” that is used by the particular organization. For example, mimic the exact signature of the user whom he spoofs his identity.
Choosing the particular human weakness that will be exploited by using social engineering.
The attacker will need to decide about the specific “human weakness” that he is going to target.
For example
- Greed – inform the victim that he is the winter in some lottery, if you click on this link, you will win a big prize, get a free trial and so on.
- Curiosity – learn the secret of losing 10 kilos in 10 days.
- Humanity – if you click this link, you will help hungry children.
- Fear of authority – this is your manager, please provide the following details for the next 2 hours!

In the following diagram, we can see the part of the initial phase of the Phishing mail attack

The additional part of the preparation phase could be:
- Find a website that you can attack, attack the website and “inject” malware code to the website that will infect users who will access the specific website.
- Copy the source code of a legitimate website, such as a bank website and build an identical website that looks exactly the same as the original website.
- Purchase a sibling domain name, which will use as a subtle variation of a legitimate domain name of the website that you are mimicking.
- Design and create the malware file that will be attached to the Phishing mail.
2#3 | Sending the Phishing mail phase
This is the phase in which the attacker needs to find a mail server that will be used for distributing the Phishing E-mail message.

3#3 | Executing the attack phase
The Phishing mail is just a “bridge” or a “gateway “to the main course of the meal – the specific attack that the hostile element wants to execute.
Theoretically, there is no limit to the type of “attacks” that can execute.
The most common type of attacks is:
Malware files | Virus
A very well-known and deadly attack is the “Ransomware virus” which will encrypt the local hard drive.
Malware files | Trojan
There are many types of “goals” that the attacker wants to achieve using a Trojan.
For example – some of the Trojan will enable the attacker to control remotely a particular user desktop; some of the Trojan will enable the attacker to steal the user password (keylogger); some of the Trojan will allow the attacker to convert the user desktop into a zombie machine and so on.

Another successful Phishing mail attacks are – attacks in which the victim is asked to click on a link that will lead him to a website that was created or controlled by the attacker.

Assuming that you have to manage to complete all the above steps successfully, you are entitled to describe as a “proud Phishing mail attacker”!
The next article in the current article series
Why our mail system is exposed to Spoof and Phishing mail attacks |Part 5#9



This Post Has 0 Comments