In this article, we continue to review the special characters of Office 365 Directory synchronization…
What are the possible causes for an Exchange Online mailbox deletion? | Part 3#23
In the current article, we review the possible causes that lead to a scenario, in which Exchange Online mailbox is deleted.The logical assumption is that “mailbox deletion event” not just happens, but instead, the person that acts as the Exchange Online administrator, performs the mailbox deletion consciously.
Table of contents
In reality, there are many scenarios, in which the Exchange Online mailbox “deletion event” was not planned or carried out proactively.
Instead, many of the “deletion events” occur as a result of – “Innocent administrative task,” which start a chain of events that end with the unwanted outcome of – deletion of Exchange Online mailbox.
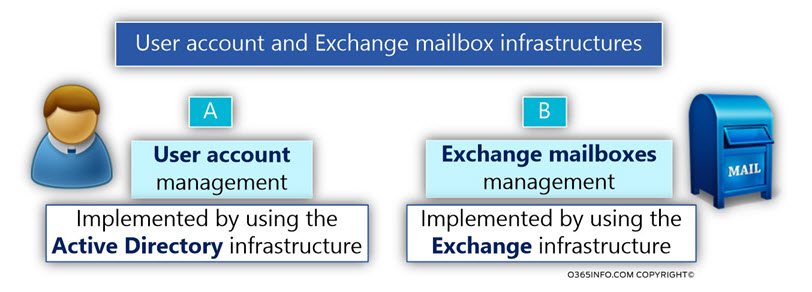
A quick reminder about the relationships that exists between user account and his Exchange mailbox
A quick reminder about the relationships that exists between the user account and his Exchange mailbox:
By default, each Exchange mailbox has a user account that is associated with the Exchange mailbox and considered as the mailbox owner.
- The infrastructure that hold \ store user accounts in Microsoft based environment is – the Active Directory.
- The infrastructure that hold \ store Exchange mailboxes in Microsoft based environment is – Exchange server.
The two primary Office 365 environments classification
In Office 365 based environment, the implementation of user account management and Exchange Online mailboxes can be classified into two major types of environments:
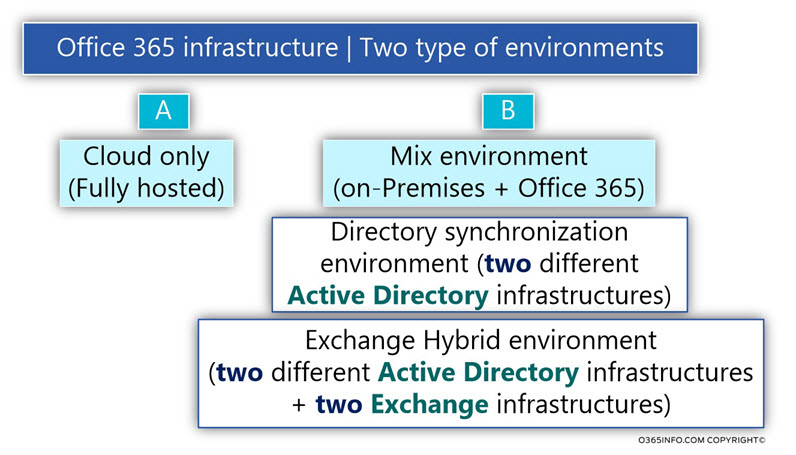
A. Cloud only (fully hosted) environment
In this scenario, Office 365 users accounts and Exchange Online mailboxes, are created and managed separately from the “organization on-Premises infrastructure.”
- The Office 365 user and group accounts are created and managed via the Office 365 – Windows Azure Active Directory infrastructure.
- The Office 365 Exchange mailboxes are created and administered via the Exchange Online infrastructure.
In this type of Office 365 implementation, the causes that can lead to an event of “Exchange mailbox deletion” are related only to Office 365 infrastructure.
For example, a scenario in which Office 365 user accounts directly deleted from the Windows Azure Active Directory or, a mailbox that directly deleted from Exchange Online.
B. Exchange Hybrid or Directory synchronization environment (Mixed environment)
The term Exchange Hybrid environment or Directory synchronized environment describes mixed environments, which consists of on-Premises environment + cloud environment. This is a “logic entity,” which distributed between two different infrastructures: on-Premises infrastructure and Office 365 infrastructure.
Using the Exchange Hybrid environment or Directory synchronized environment enables us to manage two entirely different environments and “glow” them, so they will act as a single entity.
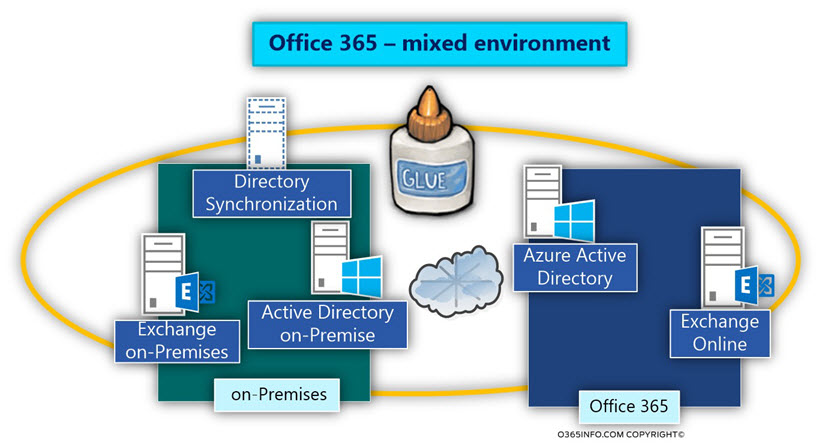
Office 365 mixed environment can be implemented using two possible scenarios:
Scenario 1 – synchronized environment (no Exchange on-Premises infrastructure).
In this scenario, the implementation of the “mixed environment,” relates only to the Active Directory services.
The On-Premise infrastructure includes the following components:
- On-Premise Active Directory
- Directory synchronization server
The On-Premise Active Directory “information” (user objects, group objects, contact objects and so on) is synchronized to the “cloud (Azure Active Directory) via the use of a dedicated component – the Directory synchronization server.
The management of the user accounts implemented by using the On-Premise Active Directory infrastructure.
The Directory synchronization server is responsible for synchronizing the different updates from the Azure Active Directory to the “cloud Active Directory” meaning Azure Active Directory.
It’s important to emphasize that in a scenario of “synchronized environment,” the On-Premises Infrastructure doesn’t include any mail infrastructure meaning – Exchange.
In this scenario, the “mail infrastructure” is implemented and managed via the Office 365 mail infrastructure – Exchange Online.
Scenario 2 – synchronized environment and Exchange Hybrid
In this scenario, the On-Premises Infrastructure includes Exchange based mail infrastructure and also, an Exchange Online mail infrastructure.
This type of scenario based on the same concepts as the previous scenario (scenario 1). The main difference is, that in case, then we use Exchange Hybrid, the mail infrastructure is “hosted” in two Parallel mail infrastructures- the on-Premises environment (Exchange on-Premises) and in the “cloud” environment meaning Exchange Online.
It’s important to emphasize that Exchange Hybrid infrastructure that defines the relationship between two separated Exchange infrastructures based on the Directory synchronization infrastructure for synchronizing the On-Premise Active Directory information to the cloud.
Direct deletion vs. indirect deletion of Exchange Online mailbox in Fully hosted and Mix environment
In the following section, we review a variety of possible scenarios which their “outcome,” is a deletion of Exchange Online mailbox.
At first glance, this definition may seem a little strange because it’s not clear what is the meaning of “outcome” or the meaning of “events” that can lead to a deletion of Exchange mailbox.
It’s easy to understand the simple scenario, in which we deliberately access Exchange Online mailbox, and deleted it.
The interesting thing is that in reality; this scenario in which Exchange Online mailbox “directly deleted” is not a typical scenario.
In other words, most of the time, the event in Exchange Online mailbox deleted, will occur as a result of “chain of events” that will lead to the “mailbox deletion scenario.”
There are many other types of scenarios, in which we don’t directly access Exchange Online mailbox and delete it, and still, a chain of events leads to the consequence of Exchange Online mailbox deletion.
Just a quick reminder – in case that the user account that considers as a mailbox owner deleted, the result is a deletion of the Exchange mailbox that associated with the user account.
To be able to classify the different scenario of – “Exchange Online mailbox deletion” I use the terms:
- Direct deletion
- Indirect deletion
This is not a formal technical term, but instead, terms that I use for simplifying the description of the different scenarios that relates to Exchange mailbox deletion.
Direct deletion
When I use the term “Direct deletion,” the meaning as the name implies, is – a scenario in which we directly access a particular “object” such as Active Directory user account or Exchange Online mailbox and delete the object.
Indirect deletion
When I use the term “Indirect deletion,” the meaning is a scenario, in which a deletion of “object A” can lead to a chain of events in which “object B” will also be deleted, and because “object B” was associated with “object C”, the outcome is that “object C” will also be deleted.
I define the deletion of “object C” as “indirect” because in this case, we didn’t directly select “object C” and deleted it, but instead, directly delete “object A” which lead to the deletion of “object C.”
I describe this phenomenon as – “Dominoes falling” because the concept of Dominoes falling based on the same concept of “Indirect deletion.”
When we line up the domino tiles and knocking the first domino tiles, the falling domino tiles, will knock the next domino tiles and so on.
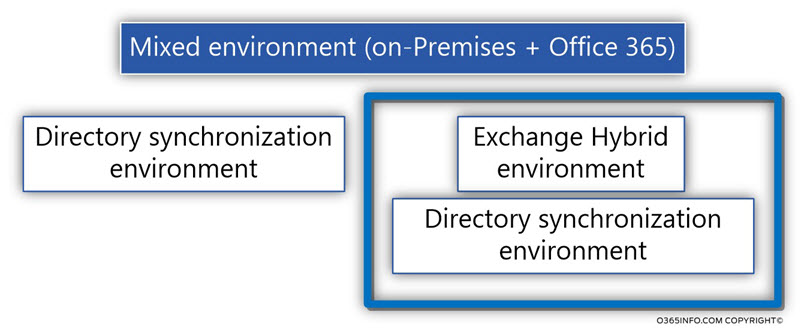
The classification of – Fully hosted vs. Mix environment
An anther classification that I would like to use is the difference between a scenario of “fully hosted” vs. the scenario of Mix environment (on-Premises + Office 365).
In case that the organization infrastructure considers as Mix environment, meaning Directory synchronization environment or Exchange Hybrid environment, the “owner” of the “user object” is the On-Premise Active Directory.
This ownership described as “source of authority.”
In this type of environment, in case that we delete On-Premise Active Directory user account, the “deletion” of the On-Premise Active Directory user account will “roll along,” and synchronized to the Azure Active Directory. The “deletion” continue the roll along to the Exchange Online infrastructure, leading to the deletion of an Exchange Online mailbox that associated with the user account.
This is a classic example of “indirect Exchange Online mailbox deletion.”
In a scenario Mixed environment (on-Premises + Office 365) the scenario of “deleting Exchange Online mailbox” will implement most of the times as – “indirect deletion.”
Direct deletion vs. indirect deletion of Exchange Online mailbox in Cloud only (Fully hosted) environment
In a fully hosted environment (no use of Directory synchronization environment or Exchange Hybrid environment), we can define three major scenarios, which can lead to an event of Exchange Online mailbox deletion.
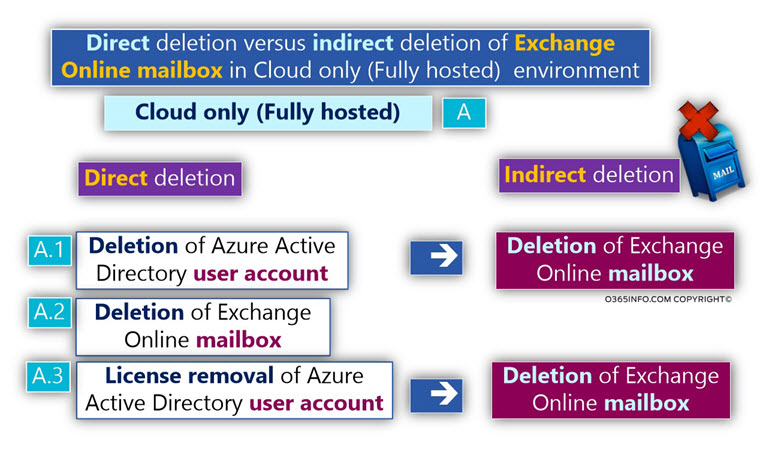
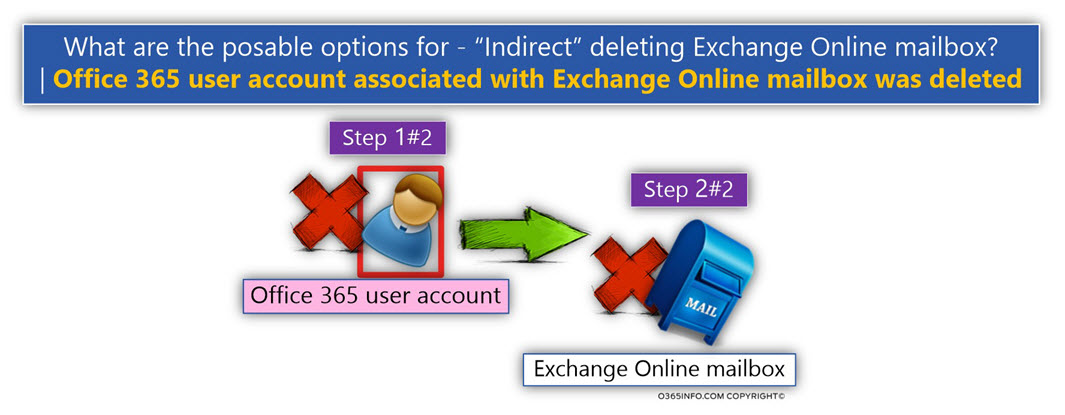
A.1 – Direct deletion 365 user account (indirect deletion of Exchange Online mailbox)
In this scenario, the deletion of Azure Active Directory user account that considers as the owner of an Exchange Online mailbox will lead to the outcome in which the Exchange Online mailbox will also deleted.
In other words – a direct deletion of Azure Active Directory user account result in – indirect deletion of Exchange Online mailbox.
How can Office 365 user account be “directly” deleted?
In Office 365 based environment, there are two ways for deleting Office 365 user account:
1. Using Office 365 admin center
Using the Active users menu, we can get a list of existing Office 365, select particular Office 365 user account and click on the – Delete user optionoption

2. Using PowerShell command
The less common option is – deleting Office 365 by using the PowerShell command:
Remove-MsolUser -UserPrincipalName <User>
A.2 – Direct deletion – Exchange Online mailbox
The term “Direct deletion of Exchange Online mailbox,” relate to a scenario, in which we select a specific Exchange Online mailbox, and Intentionally delete the mailbox.
“Indirect deletion” of Office 365 user account
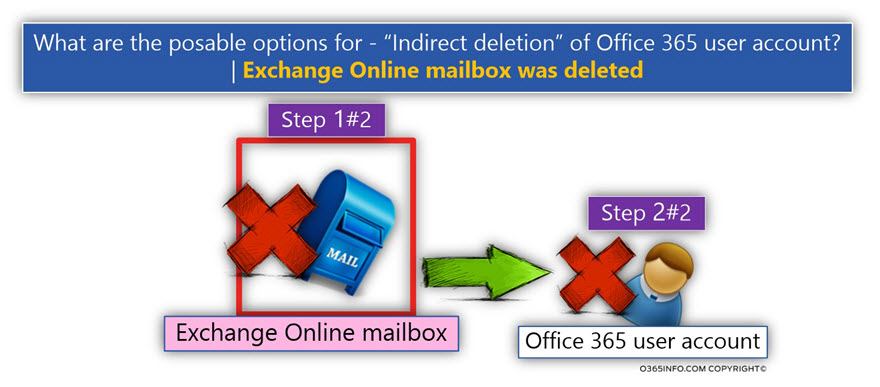
It’s important to mention that in a scenario in which we delete an Exchange Online mailbox, the outcome is that the Azure Active Directory user account that considers as the owner of the Exchange Online mailbox will also be deleted.
In other words – a direct deletion of Exchange Online mailbox, lead to indirect deletion of Windows Azure Active Directory user account.
What are the possible options for – “directly” deleting an Exchange Online mailbox?
Exchange Online Admin Center
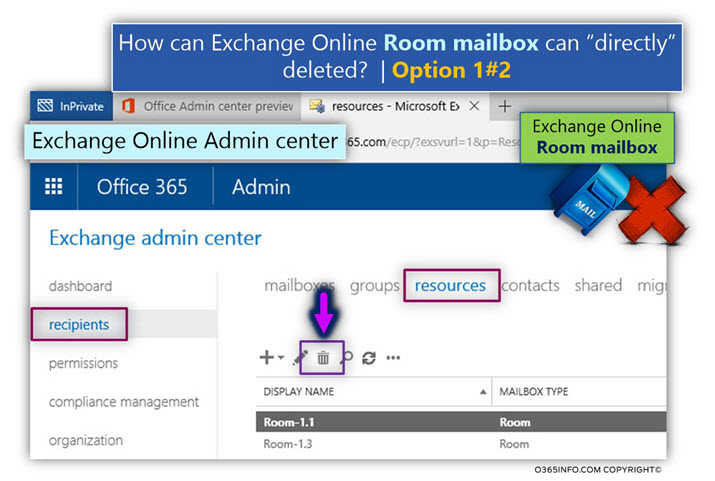
1. Deleting a resource (Room mailbox)
Option 1 – Exchange Online admin center
Deleting a resource (Room mailbox) mailbox via Exchange Online Admin center is implemented by selecting the recipients menu and then – resources menu
- Selecting the required Room mailbox.
- Click on the delete (trash can icon) option.
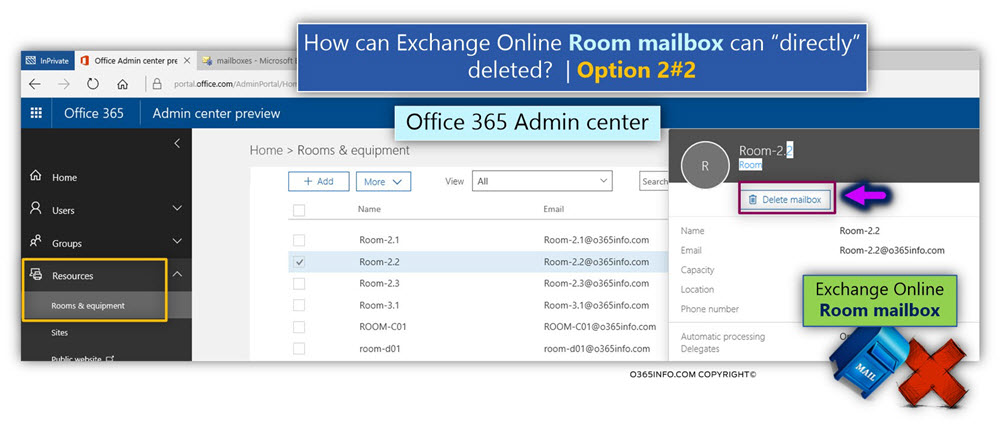
Option 2 – Office 365 Admin Center
Office 365 Admin Center includes a dedicated menu option, which enables us to manage resource (Room mailbox) mailbox, via Office 365 Admin Center.
In the following screenshot, we can see that we can select a particular Room mailbox and choose the option – Delete a mailbox.
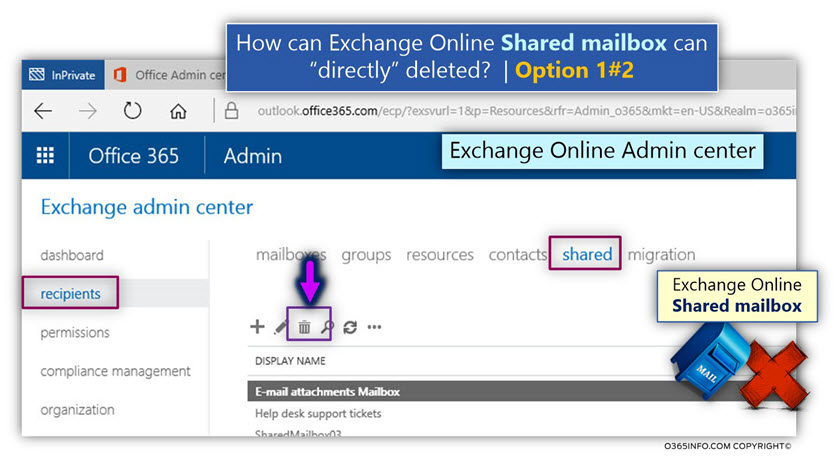
2. Deleting Shared mailbox
Option 1 – Exchange Online admin center
Deleting the resource mailbox via Exchange Online Admin center is implemented by selecting the recipients menu and then – resources menu
- Selecting the required Shared mailbox.
- Click on the delete (trash can icon) option.
Option 2 – Office 365 Admin Center
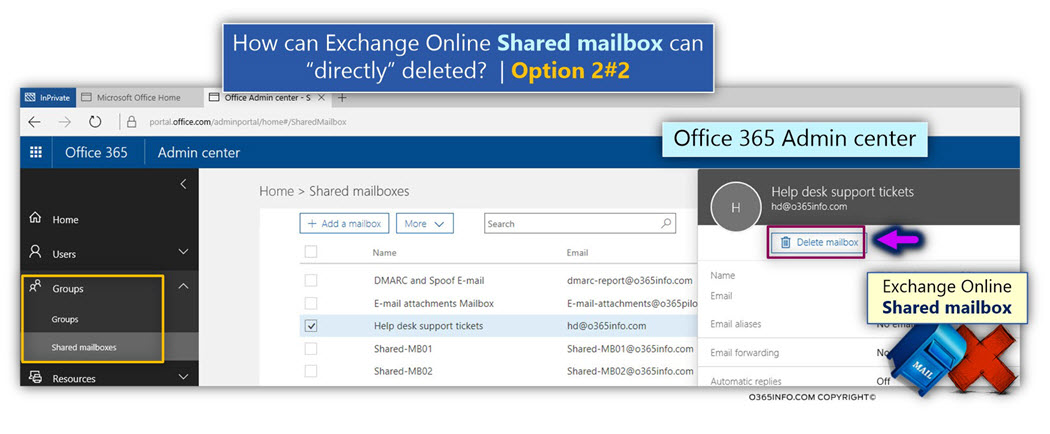
Office 365 Admin Center includes a dedicated menu option, which enables us to manage shared mailbox, via Office 365 Admin Center.
In the following screenshot, we can see that we can select a particular shared mailbox and choose the option – Delete a mailbox.
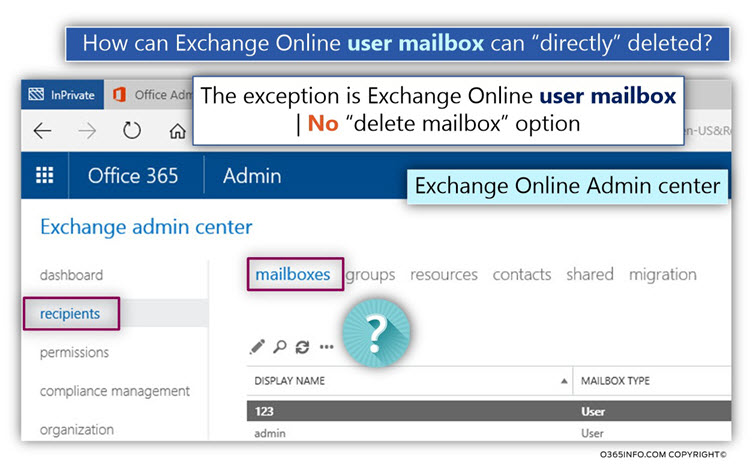
3. Deleting the user mailbox
Notice that when we use the “mailboxes” menu that displays the Exchange Online user’s mailboxes, there is no delete (trash can icon) option. In other words, we cannot delete an Exchange Online user mailbox via the Exchange Online admin center graphic interface. The only option is using the PowerShell interface.
Deleting Exchange Online mailbox using PowerShell command
The PowerShell command that we use for “directly” deleting Exchange Online mailbox is:
Remove-Mailbox <Alias>
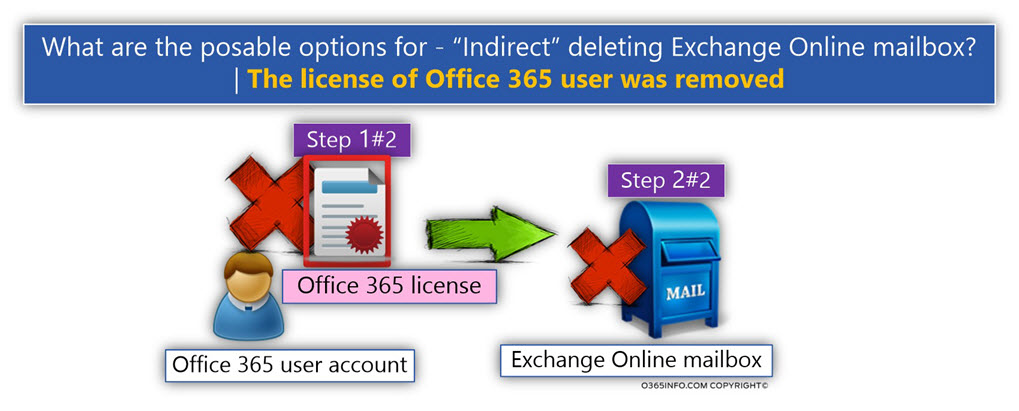
A.3 – License removal of Azure Active Directory user account
In Office 365 environment, the “charge” of Office 365 customers is, when an Office 365 license, such as – Exchange plan 1 is assigned to a particular Office 365 user account.
In case that we unassigned (remove) Office 365 license from Office 365 user accounts, the Active Directory user account continues to exist (not deleted).
But, the consequence of unassigned a license will be a deletion of Exchange Online mailbox!
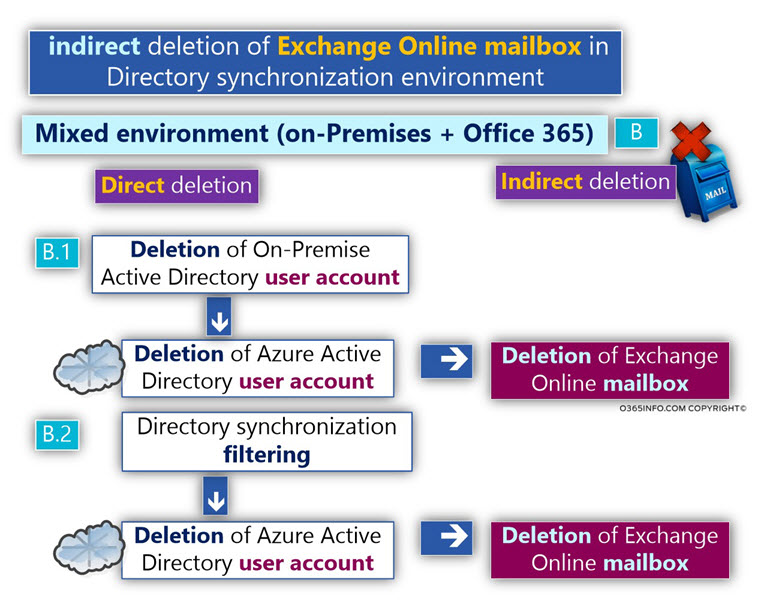
Indirect deletion of Exchange Online mailbox in Directory synchronization environment
In Office 365 implemented that described as – Directory synchronization environment or, Exchange Hybrid environment (mixed environment), we use “two sets of Active Directories” – On-Premise Active Directory + Azure Active Directory.
The On-Premise Active Directory considers as the authority that “own” the directory objects such as user account, and the Azure Active Directory consider as “replica” that gets a copy of the On-Premise Active Directory content.
The Azure Active Directory must “obey” every “command” that sent from the On-Premise Active Directory.
For example
- New objects such as a user account that created in the On-Premise Active Directory will also create in the Azure Active Directory.
- Objects such as a user account that deleted from the On-Premise Active Directory will also delete from the Azure Active Directory.

In Directory synchronization environment, the scenario of “Indirect deletion,” is implemented when a user account from the On-Premise Active Directory marked as “deleted.”
- The information about the deleted On-Premise Active Directory user account is synchronized to the cloud.
- The deletion of the On-Premise Active Directory user account, cease to Indirect deletion of the Office 365 user account.
- The deletion of the Office 365 user account, cause to Indirect deletion of – Exchange Online mailbox.
There are two scenarios in which the On-Premise Active Directory “inform” the Azure Active Directory about a scenario of a “deleted user account.”
Case 1 (B.1) – The On-Premise Active Directory user account indeed deleted
Case 2 (B.2) – A Specific Directory synchronization configuration which described as “OU filtering” which define a particular On-Premise Active Directory OU that his “content” will not replicate to the Azure Active Directory. In case that we “relocate” the On-Premise Active Directory user account to this “Filtered OU,” the information that will send to the Azure Active Directory is that the user account deleted.
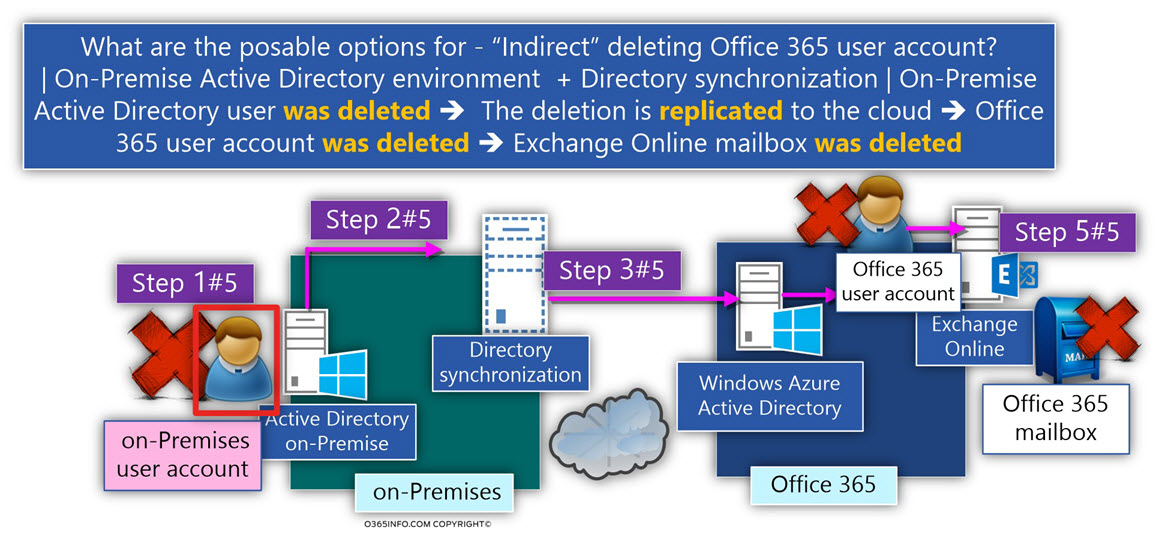
B.1 – Deletion of On-Premise Active Directory user account
In this scenario, a deletion of On-Premise Active Directory user account will start a chain of events, which lead to the deletion of Exchange Online mailbox.
To be able to understand better the relationships between these two distinct environments, let’s use the following scenario:
- Bob user account created in On-Premise Active Directory.
- Directory synchronization services (AD connect server located in the On-Premises), replicate the information about “Bob user account” to the Windows Azure Active Directory and Bob’s account was created in the Azure Active Directory (the Office 365 entity of Bob)
- An Exchange Online license was assigned to the “Office 365 Bob user account.”
- Thus, an Exchange Online mailbox was automatically created, and “attached” to Bob’s user account (the Azure Active Directory user account).
An organization help desk team member accidentally delete “Bob On-Premise” Active Directory user account.
- Directory synchronization services replicate the information about the “deletion” of “Bob user account,” to the Windows Azure Active Directory.
- The Azure Active Directory “must” also delete “Bob Office 365 user account”.
- Windows Azure Active Directory replicates the information to the Exchange Online infrastructure.
- Exchange Online must delete Bob’s
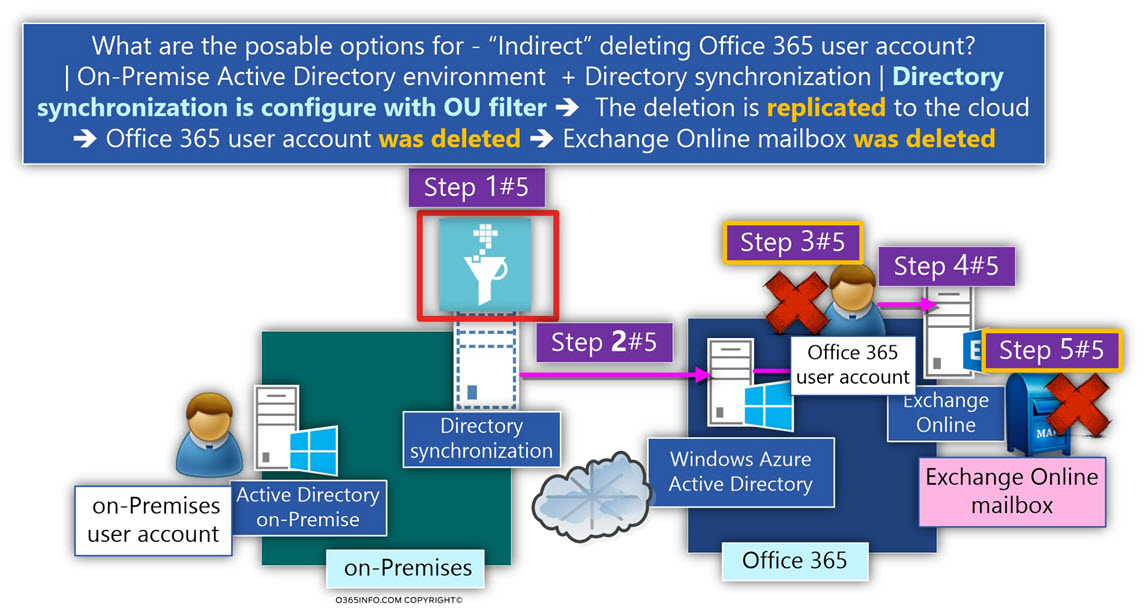
B.2 – Directory synchronization filter
The purpose of the directory synchronization infrastructure is – to synchronize On-Premise Active Directory objects such as a user account in the cloud (Windows Azure Active Directory).
When relating to the Directory synchronization infrastructure, the term “Filter” used for describing a particular configuration setting, in which we “instruct” the directory synchronization server not to synchronize a specific object\s to the cloud.
The directory synchronization filter can implement at various levels, such as – specific user account, specific properties or specific OU.
In case that we want to apply the option of – “Directory synchronization filters,” the recommended option is to add all the required filters before we start the synchronization process from the On-Premise Active Directory to the cloud (Windows Azure Active Directory).
The reason for this recommendation is that in case that we already start the process of Directory synchronization and some Directory synchronization filter later, All the objects that meet the filter criteria will deleted from the Windows Azure Active Directory.
For example:
- John is working at marketing department.
- John Active Directory user account was synchronized to the cloud, and we assign Exchange Online license to John.
- Later, we will create a Directory synchronization filter, which excludes (filter) all the employees who work in the marketing department from the synchronization process.
- The information about the “filtered object” synchronized with the Directory synchronization server to the Windows Azure Active Directory as a “deletion operation.”
The meaning is that is our particular scenario, John Office 365 user account will be deleted, and as we know, the John Exchange Online mailbox will be also deleted.
The next article in the current article series
What are the possible options for recovering Exchange Online mailbox? | Part 4#23