The current article is the third article of four articles series, on the subject of…
Exchange 2013 coexistence | Autodiscover infrastructure | Part 1/2 | 11#23
In the following article, we will review the subject of Autodiscover infrastructure in an Exchange 2013 CAS environment. In a modern Exchange environment, we can say that the Autodiscover services consider the foundation for all the rest of the various Exchange infrastructure.The Exchange Autodiscover architecture can consider as complex and sophisticated, especially in an Exchange 2013 coexistence environment.
My underlying assumption is that: you (my reader) are familiar with the concept of Exchange Autodiscover and what does the Autodiscover “do”. But a quick review of the Autodiscover infrastructure will not kill anyone.
The article is the first of two, in which we will review the subject of Autodiscover infrastructure in an Exchange 2013 coexistence environment. The next article is Exchange 2013 coexistence environment | Autodiscover infrastructure | Part 2/2
Table of contents
- Exchange Autodiscover service | The element, the components and charters
- Exchange Autodiscover and Exchange 2013 coexistence environment
- The concept of: Exchange 2013 CAS as an Autodiscover focal point
- The content of the Autodiscover file
- External and internal Exchange client | Exchange 2013 CAS as Autodiscover Endpoint
- Public Exchange infrastructure and Autodiscover services
- Exchange CAS 2013 – the Successor of legacy Exchange CAS servers
Exchange Autodiscover service | The element, the components and charters
Exchange clients completely depend upon the Exchange Autodiscover services.
Let’s start with a few observations about the Exchange Autodiscover infrastructure:
1. The element that provides the Autodiscover information to Exchange clients.
The element that needs to “feed” the Exchange clients with the Autodiscover information is: “Exchange CAS server.”
2. Autodiscover dynamic data\information
The Autodiscover data\information is not a “static information”. Instead, the Autodiscover considered as a dynamic information that is generated each time for each of the Exchange clients.
3. The element that generates the Autodiscover information.
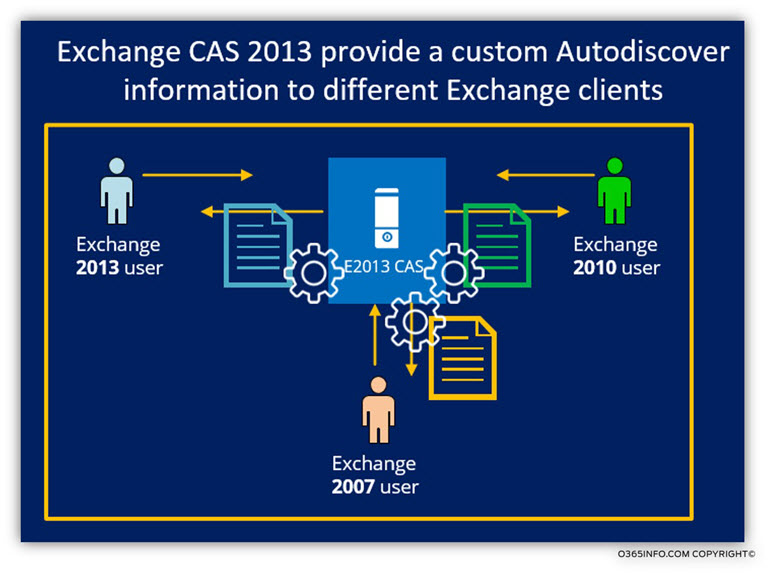
In previous versions of Exchange: Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010, the “element” that was responsible for generating the Autodiscover information was the Exchange the hold the Exchange CAS server role.
In the Exchange 2013 environment, the component that generates the Autodiscover information is the Exchange 2013 that holds the Exchange Mailbox role. Exchange 2013 CAS server is responsible for “delivering the Autodiscover information and Exchange Mailbox server is in charge of “creating” the Autodiscover information.
4. Autodiscover content | Exchange coexistence environment
As mentioned, the Autodiscover information considers as a “dynamic data” because the Autodiscover data customized for each of the different types of Exchange client version. For example, the Autodiscover information that provided to the Exchange 2007 clients (an Exchange client that his mailbox hosted on Exchange 2007 Mailbox server) is different than the Autodiscover information that given to the Exchange 2013 clients (an Exchange client that his mailbox hosted on Exchange 2013 Mailbox server).
5. Autodiscover content | External vs. internal Exchange client
The Autodiscover information that Exchange CAS servers provide to his client depends on the “physical location” of the Exchange client. In case that the Exchange CAS server recognizes that the Exchange client considered as “internal client,” the Autodiscover information that provided to the Exchange client, will include information about internal resources.
The meaning of “internal resources” is – FQDN and URL address that includes “internal names” of Exchange servers. Internal Exchange names are not “exposed” to the public network or in other words, an external Exchange mail client cannot “reach” these Exchange servers.
In case that the Exchange CAS server recognizes that the Exchange client considers as “external client,” the Autodiscover information that provided to the client, will include information about external resources.
The meaning of “external resources” is – information about Public facing Exchange CAS server\s. The information will include public FQDN + URL address.
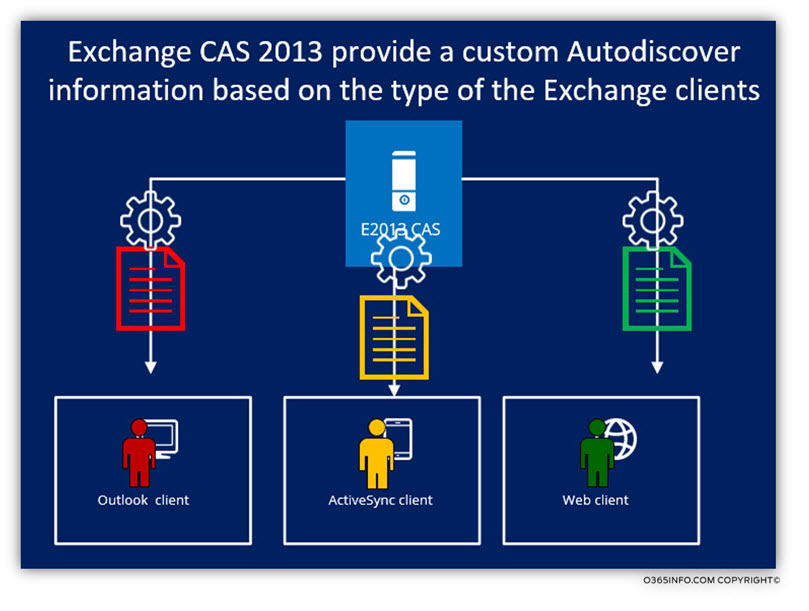
6. Autodiscover content | Different mail client (mail protocols)
The Autodiscover information, which Exchange CAS server provide to his client, depends on the “type” of the Exchange client.
The meaning of the term: ”different mail client” is related to mail clients such as OWA mail client, Mobile (ActiveSync) mail client and Outlook mail client. Each of this mail clients uses different communication protocol and uses the Exchange Autodiscover in a different way.
For example Outlook client use a protocol such as – RPC, RPC over HTTP, and MAPI over HTTP vs. mobile Exchange client that uses the ActiveSync protocol.
The Autodiscover information that Exchange provides two “different type of Exchange clients” is not identical. For example – the Autodiscover information that provided to mobile Exchange client (ActiveSync client) is different than the Autodiscover information that given to the Outlook client.
Exchange Autodiscover and Exchange 2013 coexistence environment
From the information that we are reviewing in the previous section, it’s clear that the “job” of providing Autodiscover information is not simply because, there are many elements and factors that are involved in the Autodiscover infrastructure.
In an Exchange 2013 coexistence environment, we add an element to this complex environment because in an Exchange coexistence environment, there a couple of Exchange CAS servers that can provide Autodiscover information\services.
So now, we need to understand how Exchange 2013 “fits” into the Autodiscover infrastructure and what are the required changes or updates that need to implement in an Exchange 2013 coexistence environment.
To be able to clarify that the subject of Autodiscover infrastructure and Exchange 2013 coexistence environment, let’s divide the Exchange infrastructure into two parts:
- Public Exchange infrastructure and Autodiscover services
- Internal Exchange infrastructure and Autodiscover services
The concept of: Exchange 2013 CAS as an Autodiscover focal point
To be able to understand better the Autodiscover infrastructure in an Exchange environment, it’s important to understand the concept which I described as: “Exchange Autodiscover focal point”. The meaning of this concept is that the Exchange 2013 CAS needs to be configured as the “main Autodiscover point” or the “primary Autodiscover point” relates to the realm of:
- The type of Exchange clients – the Exchange 2013 CAS will need to be configured as an Autodiscover Endpoint and serve, all the types of Exchange client that exists in Exchange 2013 CAS such as: Exchange 2013 client, Exchange 2010 client and Exchange 2007 clients.
- External and internal Exchange client – Exchange 2013 CAS will need to be configured as an Autodiscover Endpoint and serve External and internal Exchange clients.
The content of the Autodiscover file
Throughout this article and the rest of the article in this article series, we will mention many time terms such as: Autodiscover information, Autodiscover response, etc.
The important thing that we will need to understand is that the Autodiscover information that is provided by the Exchange CAS server to “his” Autodiscover client is not a “static file” but instead the opposite.
The Autodiscover “answer” that the Exchange CAS server provides is generated each time in a unique way for each of the separated Autodiscover client requests.
We can say that the Exchange CAS server is tailoring the Autodiscover Suit based on the very precise measurements of his Autodiscover client.
The Autodiscover “answer” that the Exchange CAS 2013 provides to the Autodiscover client depends on two major factors:
1. The Exchange client version
The meaning of the term “Exchange client version”, is the Exchange mailbox server version for host the mailbox of a specific Exchange client user. For example, when we use the term: Exchange 2007 client, the meaning is Exchange client that his mailbox hosted on the Exchange 2007 mailbox server.
The information that appears in the “Autodiscover answer” that sent to the Autodiscover client customized to the particular version of the Exchange client.
In the following diagram, we can see that the Exchange CAS 2013 is generating a custom Autodiscover answer for each of the different Autodiscover clients.
For example, the content with the Autodiscover information that provided to the Exchange 2007 client is different than the substance of the Autodiscover information that given to the Exchange 2013 clients.
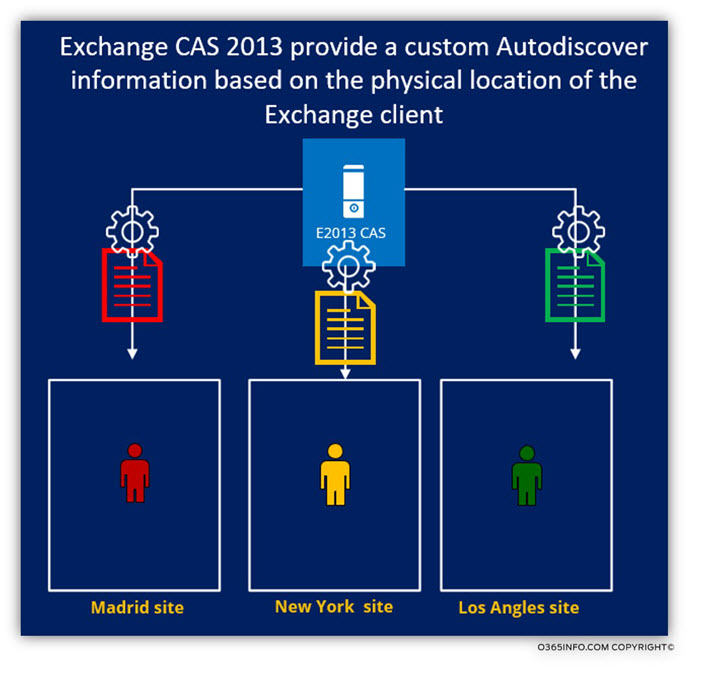
2. The Exchange client “physical location”
The term “Exchange client physical location” relate to the location from which the Exchange CAS server address or connect the Exchange CAS server.
The primary classification for Exchange client “location” is – internal Exchange infrastructure vs. public Exchange infrastructure. The “roles” that apply to these two distinct Exchange environments are different, the charter of the communication channel between the Exchange client, and his Exchange CAS server is different, and the Autodiscover information that provided to the internal Exchange client is distinct from the Autodiscover information that provided to external Exchange client.
An additional classification that we can use that relates to “internal Exchange clients” is the Exchange site or the Active Directory site in which they physically located.
For example: in a scenario of multiple Exchange sites, the Autodiscover information that the Exchange CAS server provides includes an accurate “Exchange site information”. For example, in case that the Autodiscover client is an Exchange client from Madrid site, the Autodiscover information that provided to the Exchange client, will include information (URL address, host name, etc.) of Exchange resources that located at the Madrid site.
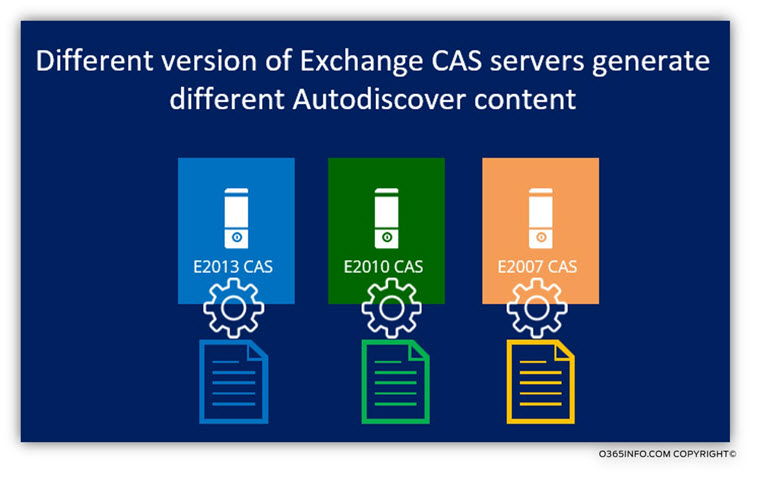
3. The Exchange server version
The Autodiscover content, depend on the version of the Exchange server who provides the Autodiscover information.
For example – Exchange CAS 2013 is more “advanced” than the previous version of Exchange CAS servers and the Autodiscover information that he provides to his clients, include additional parameters and connection methods.
For example, Exchange CAS 2013 provides other “section” in the Autodiscover information that described as – EXHTTP
For these reasons, it’s important that all the Exchange clients (the different versions of Exchange clients) will address only the Exchange CAS 2013 for Autodiscover information. Additionally, the Outlook client software version will be updated to enable the Outlook client to “understand” the new language” that the Exchange CAS 2013 use.
4. The Exchange client type
Additional factors that affect the content if the Autodiscover information that Exchange CAS server provide is the “type” of the Exchange client. Technically, all the Exchange client types: Outlook, ActiveSync, and OWA, use the Autodiscover infrastructure, but the “main Autodiscover client” is Outlook and second is the ActiveSync Exchange client.
When Exchange CAS server recognizes that the Exchange client is Outlook or a “Mobile client” (ActiveSync), the Autodiscover information that the Exchange CAS server generates is different because each of these clients needs different parameters, etc.
External and internal Exchange client | Exchange 2013 CAS as Autodiscover Endpoint
1. Public Exchange infrastructure the concept of: “central Autodiscover point” in Public Exchange environment, is not a new concept.
The realization of this concept is as follows: even if the Exchange public infrastructure, consists of multiple Public facing Exchange sites, the Autodiscover service will always be “pointed” into a single focal point.
In other words, although in theory each of the Public facing Exchange sites can provide Autodiscover services, the Autodiscover service will be based on a central concept. Only one particular Public facing Exchange CAS server or to be more accurate, one specific Public facing Exchange CAS server, will be responsible for providing the Autodiscover services for all the Exchange clients from the different Exchange sites.
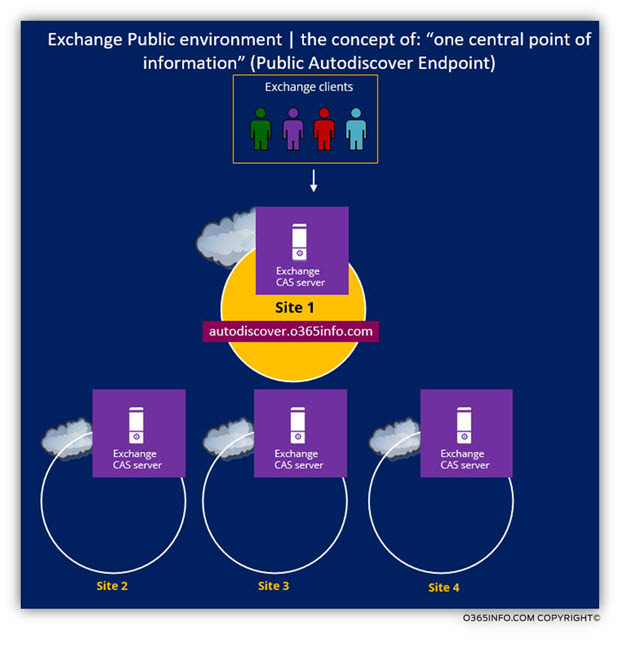
Note: there is an exception to the concept of “Exchange Autodiscover focal point” in a public environment in a scenario of GeoDns that is based upon a multiple “Autodiscover points”. The Exchange clients (the Autodiscover client) will be pointed to their Public facing Exchange CAS server based on their geographical location.
2. Internal Exchange infrastructure in an Exchange 2013 coexistence environment.
The concept of “Exchange Autodiscover focal point” is also implemented, on the internal Exchange environment in a scenario of the Exchange 2013 coexistence environment. In an Exchange coexistence environment, we are using two or three different Exchange server versions. Although since Exchange 2007 version, each of the Exchange server “knows” how to use the Autodiscover infrastructure, there a significant difference between each of the Exchange server versions (Exchange 2007, 2010 and 2013).
This “deference” relates to many “parts” and also to the Autodiscover architecture and implementation. To be able to “unified” the different Exchange versions, another concept which I derived as: “backward compatibility” is implemented. The “backward compatibility” concept applied by using the ”newer Exchange server version” as an Autodiscover focal point.
For example, in an Exchange site that uses an Exchange 2013 coexistence environment which includes Exchange 2007 servers and Exchange 2010 servers, the Autodiscover infrastructure will be “pointed” to the Exchange 2013 CAS server.
Public Exchange infrastructure and Autodiscover services
To be able to demonstrate the concept of Exchange Autodiscover in a Public environment, let’s use the following scenario: An organization that has three Public facing Exchange sites.
- Site 1 and site 3 are “Public facing Exchange sites” and site 2 is an internal Exchange site (non-public site).
- The organization Public domain name is: o365info.com
- The public Autodiscover record is: autodiscover.o365info.com
General concept of Autodiscover client protocol connectivity flow
When an external Exchange user looks for an Autodiscover Endpoint (Public facing Exchange CAS server), the Autodiscover record (autodiscover.o365info.com), will point the Exchange clients to the Public facing Exchange CAS server in site 1.
- Scenario 1: User mailbox hosted on Exchange Mailbox servers is site 1.
The Autodiscover information that Exchange CAS server in site 1 will provide includes the information about the “site 1 public Exchange infrastructure” (URL address with the public FQDN of the Public facing Exchange CAS server in site 1).Each of the Exchange client requests will be accepted by the Public facing Exchange CAS server in site 1 and will be proxied by the public facing Exchange CAS server to “internal Exchange infrastructure” such as the Exchange Mailbox server in site 1. - Scenario 2: User mailbox hosted on Exchange Mailbox servers is site 2
because, site 2, is not a Public facing Exchange site (Intranet site), the Autodiscover information that Exchange CAS server in site 1 will provide, includes the information about the “site 1 public Exchange infrastructure” (URL address with the public FQDN of the Public facing Exchange CAS server in site 1).
Each of the Exchange client requests accepted by the Public facing Exchange CAS server in site 1 and, will be proxied by Public facing Exchange CAS server to the internal\private Exchange infrastructure in site 2. - Scenario 3: User mailbox hosted on Exchange Mailbox servers is site 3.
Because site 3, is a Public facing Exchange site, the Autodiscover information that Exchange CAS server in site 1 will provide, includes the information about the “site 3 public Exchange infrastructure” (URL address with the public FQDN of the Public facing Exchange CAS server in site 3).The “site 3 Exchange client” gets the Autodiscover information, which includes the URL address with the public FQDN of the Public facing Exchange CAS server in site 3. From now on, the “site 3 Exchange client” will address directly the Public facing Exchange CAS server in site 3.
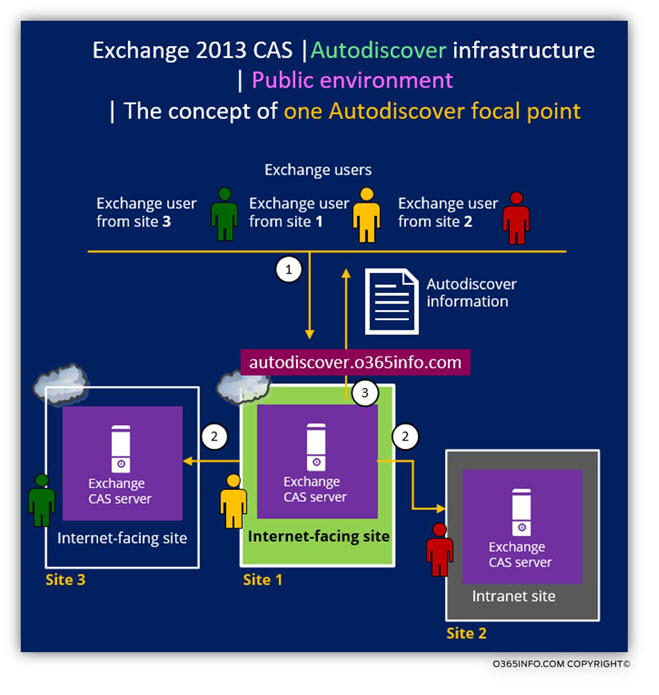
Note: there are exceptions to this description such as ActiveSync clients.
Exchange CAS 2013 – the Successor of legacy Exchange CAS servers
In an Exchange 2013 coexistence environment, the Exchange 2013 CAS server serves as an Autodiscover Endpoint for all the different Exchange clients.
Exchange CAS 2013 server will “replaces’” or “Inherits” the role of the legacy versions of Exchange CAS server, such as – Exchange 2007 CAS, or Exchange 2010 CAS.
The reason for this “replacement” is because the Exchange CAS 2013 server can handle Autodiscover request from all the different Exchange clients – native Exchange 2013 Autodiscover clientS. At the same time, Exchange CAS 2013 server, will “know what do” with an Autodiscover request of legacy Exchange clients such as – Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010 clients.
The opposite is not true, meaning: Exchange 2007, 2010 CAS server will not handle an Autodiscover request of “advanced Exchange clients” such as Exchange 2013 clients correctly.
To be able to demonstrate the concept of Public facing Exchange 2013 CAS in Exchange 2013 coexistence environment, let’s use the following scenario: A company, which has one Public facing Exchange sites.
Note – in the current scenario, we will demonstrate the Autodiscover connectivity flow by using a scenario of a company that has only one Public facing Exchange sites.
I avoid from using the charters of the previous scenario (a scenario in which the corporation has multiple Public facing Exchange sites) to simplify the logic and the understanding if the Autodiscover connectivity flow in a public environment + an Exchange environment that described as Exchange 2013 coexistence environment.
- The company Exchange site is based on Exchange 2013 coexistence environment, which includes the following Exchange server versions: Exchange 2007, Exchange 2010 and Exchange 2013.
- The organization Public domain name is: o365info.com
- The public Autodiscover record is: autodiscover.o365info.com
- The legacy Exchange 2007 namespace is: legacy.mail.o365info.com
When an external Exchange user looks for an Autodiscover Endpoint (Public facing Exchange CAS server), the Autodiscover record (autodiscover.o365info.com), will point the Exchange clients to the Exchange 2013 Public facing Exchange CAS server.
In most of the “best-practice implementation” of Exchange 2013 coexistence environment, the Autodiscover information that provided to Exchange 2010 clients, and Exchange 2013 clients are identical.
The Autodiscover information process and infrastructure that implemented with an Exchange 2007 client are different because the Autodiscover information will include “pointers” to the Exchange 2007 infrastructure that will be “represented” by the legacy namespace.
Scenario 1: Exchange 2013/2010 Client (User mailbox hosted on Exchange 2013 or Exchange 2010 Mailbox server).
When the Public facing Exchange 2013 CAS server recognizes that the Autodiscover client is Exchange 2013/2010 client, the Autodiscover information that the Exchange 2013 CAS provides, includes the “public URL address” of the different Exchange services that in our scenario, point to the same Public facing Exchange 20123 CAS server.
For example: the Exchange web services URL address that will appear in the Autodiscover information will be: https://mail.o365info.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx
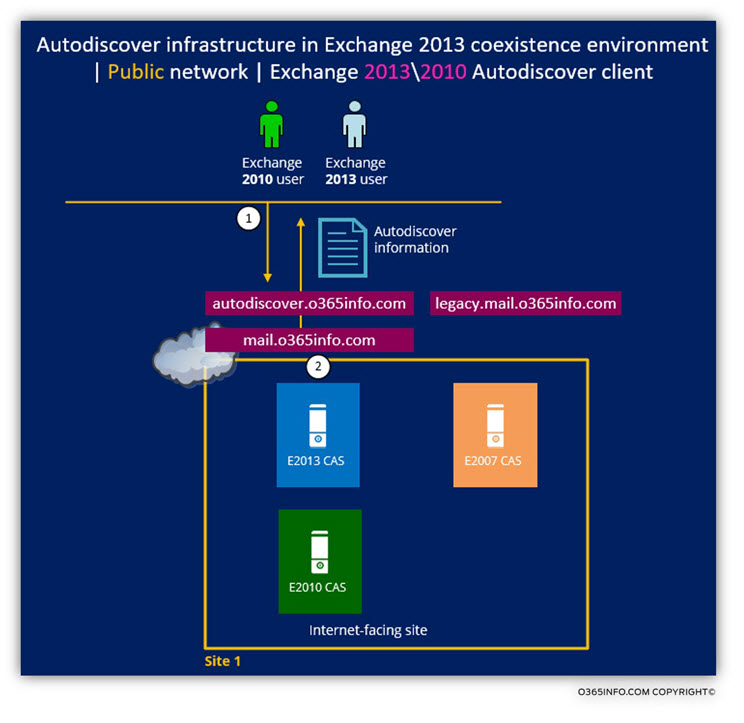
Scenario 2: Exchange 2007 client (User mailbox hosted on Exchange 2007 Mailbox server).
When the Public facing Exchange 2013 CAS server recognizes that the Autodiscover client is an Exchange 2007 client, the Autodiscover information that the Exchange 2013 CAS provides, includes URL address that will point the Exchange 2007 clients to the Public facing Exchange 2007 CAS server.
The Exchange 2007 client, “gets the Autodiscover information” that includes the URL address with the public legacy FQDN of the Public facing Exchange 2007 CAS server. When the Exchange 2007 client (such as Outlook client), needs to use a particular Exchange web service, the Exchange 2007 client will use the public legacy namespace of the Exchange 2007 CAS.
For example – the Exchange web services URL address that will appear in the Autodiscover information will be: https://mail.o365info.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx



This Post Has 0 Comments